Answers
Answer:
km = 3.24
m = 3,240
dm = 32,400
Explanation:
km = 1000m
m = 10dm
Explanation:
take a look carefully hope it will help u
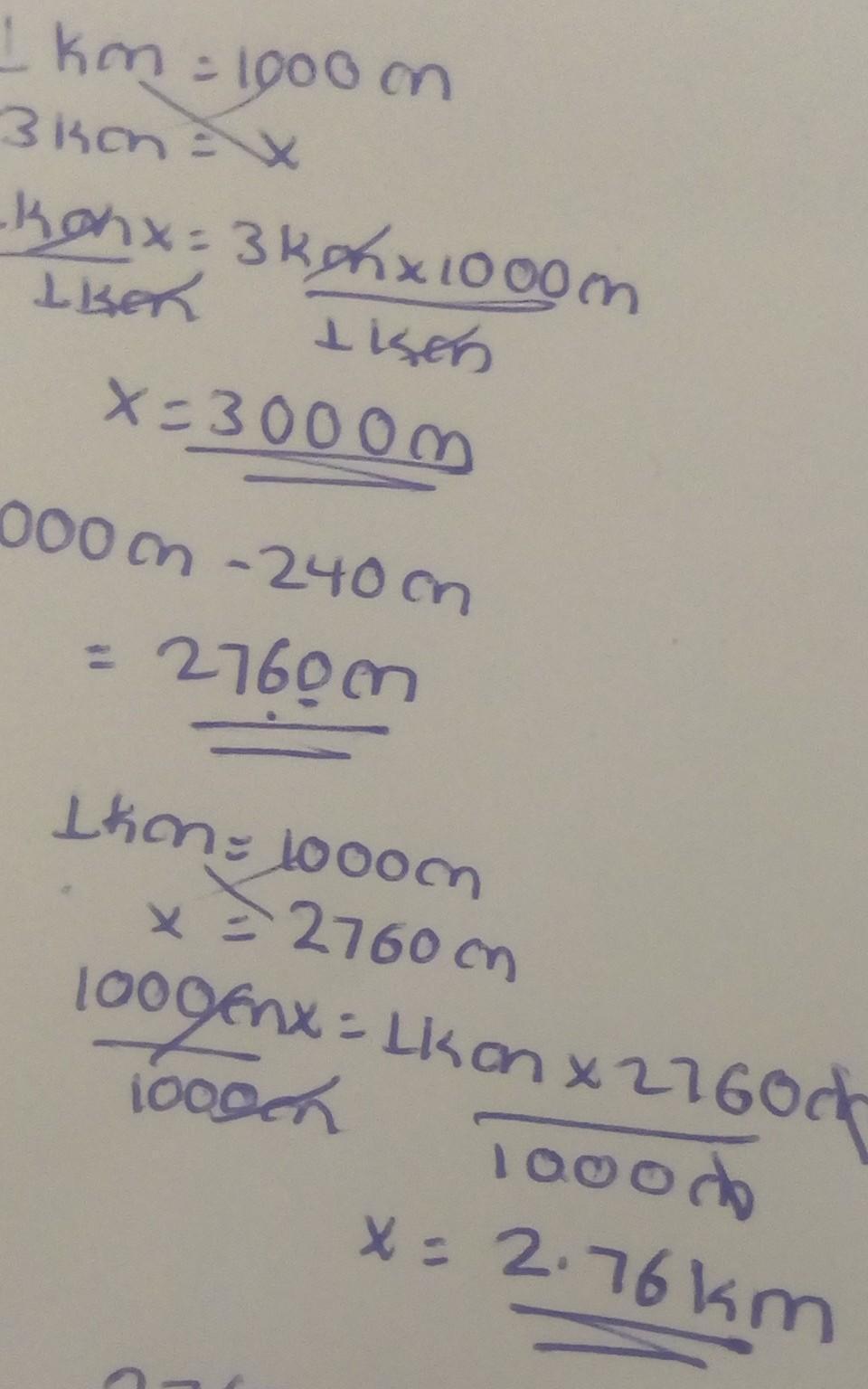

Related Questions
When a tennis ball is spun around in a circle on a string and the string breaks the tennis ball
will be pulled in a curved path away from the center because of Centrifugal force
True or false
Answers
Answer:
False
whenever the string breaks, the ball will follow the straight line tangential path
Explanation:
No, the ball will not follow a curved path after the string breaks. Since, the the direction of velocity is tangential to each point of the circular motion. Therefore, it changes at every point. This produces an acceleration in the circle called centripetal acceleration. There is also a tangential component of acceleration acting on the ball during this motion.
So, whenever the string breaks, the ball will follow the straight line tangential path. Hence, the given statement is false.
In a tug of war, team A pulls the rope with a force of 50 N to the right and team B pulls it with a force of 110 N to the left. What is the resultant force on the rope and which direction does the rope move? (N represents newton, the unit of force)
Answers
Given that,
Force in right side = 50 N
Force in left side = 110 N
To find,
The resultant and direction of force.
Solution,
Let the net force F is acting on the rope. Also, we can assume that right side is positive and left side is negative.
F = 50+(-110)
= -60 N
So, the magnitude of the resultant force acting on the rope is 60 N and it acts in left side.
Runner A is initially 8.0 mi west of a flagpole and is running with a constant velocity of 7.0 mi/h due east. Runner B is initially 8.0 mi east of the flagpole and is running with a constant velocity of 6.0 mi/h due
west. How far are the runners from the flagpole when they meet?
Answers
The runners meet at 0.615mi away from the flagpole due to constant velocity.
Velocity informs us of the rate of change of your position, or how quickly your location is altering in relation to time. The difference between your end and beginning positions is referred to as displacement in physics, and velocity is defined as displacement divided by time. Additionally, an object is considered to be moving with constant velocity if it covers the same distance every second.
A vector is a speed that is constant. For a quantity to be fully described, it needs both a magnitude and a direction. Distance per time units is defined as constant velocity. The velocity tells you how quickly your distance is changing per unit of time or how quickly your location is changing.
To learn more about constant velocity please visit-
https://brainly.com/question/10217879
#SPJ9
A bullet is fired horizontally at a height of 2 meters at a velocity of 930 m/s. Assume no air resistance. How far did the bullet travel horizontally when it hit the ground?
595.2 m
478.4 m
364.0 m
247.2 m
Answers
Answer:
im pretty sure its a
Explanation:
Suppose you exert a force of 180 N tangential to a 0.280-m-radius, 75.0-kg grindstone (a solid disk). (a)What torque is exerted
Answers
Answer:
[tex]\tau = 50.4Nm\\[/tex]
Explanation:
Torque is expressed according to the formula;
[tex]\tau = Fr\\[/tex]
F is the force exerted
r is the radius
Given
F = 180N
r = 0.280m
Required
Torque
Substitute into the formula and get torque
[tex]\tau = 180 \times 0.280\\\tau = 50.4Nm\\[/tex]
Hence the torque exerted is 50.4Nm
A marble is fired from a spring-loaded gun at an angle of 30◦
above the ground and reaches a
maximum height 500m.
a. What is the velocity of the marble at it’s maximum height?
b. What is the acceleration of the marble at it’s maximum height?
c. What was the marbles initial velocity?
d. How long did it take for the marble to reach it’s maximum height?
Answers
Answer:
jrirnr tn
Explanation:
and then we was just wondering what we should be talking to about to see how you are
An ice skater applies a horizontal force to a 150 N block on frictionless, level ice, causing the block to accelerate uniformly at to the right. After the skater
stops pushing the block, it slides onto a region of ice that is covered with a thin layer of sand. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the
sand-covered ice is 0.36.
Calculate the magnitude of the force of friction acting on the block as it slides over the sand-covered ice
Answers
Answer:
The friction force has a magnitude of 54 N and points to the left
Explanation:
Friction Force
When an object is moving and encounters friction in the air or rough surfaces, it loses acceleration because the friction force opposes motion.
The friction force when an object is moving on a horizontal surface is calculated by:
[tex]Fr=\mu N[/tex]
Where \mu is the coefficient of static or kinetics friction and N is the normal force.
If no forces other then the weight and the normal are acting upon the y-direction, then the weight and the normal are equal in magnitude:
N = W
Thus, the friction force is:
[tex]Fr=\mu W[/tex]
The ice skater accelerates a block to the right on frictionless horizontal ice and then stops pushing it. The block continues to move at a constant speed when it finds a sand-covered surface with a kinetic coefficient of friction of 0.36.
The friction force is:
Fr=0.36*150
Fr = 54 N
The friction force has a magnitude of 54 N and points to the left
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
6
Karen wants to pump up her car tyre.
Her pump has a piston with an area of 7 cm^2
175 N
area = 7 cm^2
Karen pushes the handle down with a force of 175 N.
(a)
What pressure does she exert on the air in the pump?
Answers
Answer:
250000Pa
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Force applied = 175N
Area = 7cm²
Unknown:
Pressure exerted by the air in the pump = ?
Solution:
Pressure is the force per unit area acting on a body;
Pressure = [tex]\frac{force }{area}[/tex]
Area = 7cm² ;
10000cm² = 1m²
7cm² is 7 x 10⁻⁴m²
Pressure = [tex]\frac{175}{0.0007}[/tex] = 250000Pa
0
Northeast
North Central
South
Region of the United States
West
●
8 Claims Evidence Reasoning Which
region of the country has the coldest
January temperatures? Use the data in the
graph to support your claim, and explain
Answers
A daring squirrel runs toward a cat, then turns around to safety. A graph of its velocity over time is shown
below.
Answers
Answer:
it's 1.0
Explanation:
kahn academee
Energy stored because of an object's height above the Earth's surface is_____energy.
nuclear
gravitational
electrical or chemical
Answers
Answer5 ms 3. A football player has a mass of 95 kg, and he is running with a velocity of 15 m/s. What is his momentum? Answer:
Answers
Answer:
1425kgm/s
Explanation:
Given parameters:
Mass = 95kg
Velocity = 15m/s
Unknown:
Momentum = ?
Solution:
The momentum of a body is the amount of motion it posses;
Momentum = mass x velocity
Insert the parameters and solve;
Momentum = 95 x 15 = 1425kgm/s
Starting with the definitions of momentum and kinetic energy, derive an equation for the kinetic energy of a particle expressed as a function of its momentum.
Answers
Answer:
[tex]K.E = (\frac{1}{2})Pv[/tex]
Explanation:
The momentum of a particle is defined as the product of its mass and velocity:
[tex]P = mv[/tex] -------------------- equation (1)
where,
P = momentum of the particle
m = mass of the particle
v = velocity of the particle
The kinetic energy of the particle is given as follows:
[tex]K.E = (\frac{1}{2})mv^2\\\\K.E = (\frac{1}{2})v(mv)[/tex]
using equation (1), we get:
[tex]K.E = (\frac{1}{2})Pv[/tex]
A ball is tied to the end of a cable of negligible mass. The ball is spun in a circle with a radius 7.1 m making 3.9 revolutions every 9.4 second. What is the centripetal acceleration of the ball?
Answers
Answer:
48,2 m/s²
Explanation:
We're gonna use the Centripetal Acceleration formula: v² / r but before that, we got to know the velocity, that is not shown clearly to us, so....
To know the velocity let's calculate the distance that the ball traveled
The circumference of a circle formula is:
2piR
2 . 3,14 . 7,1 | That is equal to 44,588 m
We know that the ball traveled this distance 3,9 times, so...
44,588 . 3,9 = 173,8932 m
Ok, now we have the distance, just need to know the time, that is 9.4 seconds.
Velocity = Distance / Time
V = 173,8932 / 9,4
V = 18,5 (approximate)
So...
We are back to the first formula:
Ca = v² / r
Ca = 18,5² / 7.1
Ca = 48,2 m/s² (approximate)
I hope it is correct, hahaha.
If a ball leaves the ground with a velocity of 4.67 m/s,
how high does the ball travel?
Answers
Answer:
[tex]Vf^2=Vo^2+2aS\\(0m/s)^2=(4.67m/s)^2+(2*-10m/s^2)S\\-(4.67)^2 m^2/s^2=-20m/s^2*S\\S=(21.8089/20) m\\S=1.090445 m\\[/tex]
Which component of an atom contains the MAJORITY
of its mass?
Answers
Answer:
proton and neutrons
Explanation:
electron has negligible mass
What fraction of an iceberg is submerged? (ρice = 917 kg/m3, ,ρsea = 1030 kg/m3.)
Answers
Answer:
Choice d. Approximately [tex]89\%[/tex] of the volume of this iceberg would be submerged.
Explanation:
Let [tex]V_\text{ice}[/tex] denote the total volume of this iceberg. Let [tex]V_\text{submerged}[/tex] denote the volume of the portion that is under the liquid.
The mass of that iceberg would be [tex]\rho_\text{ice} \cdot V_\text{ice}[/tex]. Let [tex]g[/tex] denote the gravitational field strength ([tex]g \approx 9.81\; \rm N \cdot kg^{-1}[/tex] near the surface of the earth.) The weight of that iceberg would be: [tex]\rho_\text{ice} \cdot V_\text{ice} \cdot g[/tex].
If the iceberg is going to be lifted out of the sea, it would take water with volume [tex]V_\text{submerged}[/tex] to fill the space that the iceberg has previously taken. The mass of that much sea water would be [tex]\rho_\text{sea} \cdot V_\text{submerged}[/tex].
Archimedes' Principle suggests that the weight of that much water will be exactly equal to the buoyancy on the iceberg. By Archimedes' Principle:
[tex]\text{buoyancy} = \rho_\text{sea} \cdot V_\text{submerged} \cdot g[/tex].
The buoyancy on the iceberg should balance the weight of this iceberg. In other words:
[tex]\underbrace{\rho_\text{ice} \cdot V_\text{ice} \cdot g}_\text{weight of iceberg} = \underbrace{\rho_\text{sea} \cdot V_\text{submerged} \cdot g}_\text{buoyancy on iceberg}[/tex].
Rearrange this equation to find the ratio between [tex]V_\text{submerged}[/tex] and [tex]V_\text{ice}[/tex]:
[tex]\begin{aligned} &\frac{V_\text{submerged}}{V_\text{ice}} \\&= \frac{\rho_\text{ice} \cdot g}{\rho_\text{sea} \cdot g}\\ &= \frac{\rho_\text{ice}}{\rho_\text{sea}}\ = \frac{917\; \rm kg \cdot m^{-3}}{1030\; \rm kg \cdot m^{-3}} \approx 0.89 \end{aligned}[/tex].
In other words, [tex]89\%[/tex] of the volume of this iceberg would have been submerged for buoyancy to balance the weight of this iceberg.
why the efficiency of the single movable pully system is not 100%
Answers
Answer:
This is because part of the energy input is used to overcome gravity, inertia and friction
As the mass of a body increases, its gravitational force of attraction to the Earth...
Answers
Answer:
the answer may be mass and distance
A 125 g pendulum bob hung on a string of length 35 cm has the same period as when the bob is hung from a spring and caused to oscillate. What is the spring’s elastic constant?a) 3.5 N/mb) 5.2 N/mc) 1.9 N/md) 27 N/m
Answers
Answer:
k = 3.5 N/m
Explanation:
It is given that the time period the bob in pendulum is the same as its time period in spring mass system:
[tex]Time\ Period\ of\ Pendulum = Time\ Period\ of\ Spring-Mass\ System\\2\pi \sqrt{\frac{l}{g}} = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{m}{k}[/tex]
[tex]\frac{l}{g} = \frac{m}{k}\\\\ k = g\frac{m}{l}[/tex]
where,
k = spring constant = ?
g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s²
m = mass of bob = 125 g = 0.125 kg
l = length of pendulum = 35 cm = 0.35 m
Therefore,
[tex]k = (9.81\ m/s^2)(\frac{0.125\ kg}{0.35\ m})\\\\[/tex]
k = 3.5 N/m
Carlos is riding her bicycle. His velocity is 5 m/s to the right. His acceleration is 1.2 m/s2 to the left. He is doing what?
- moving at a constant speed
- slowing down
- speeding up
Answers
Answer:
Slowing down
Explanation:
Carlos is travelling to the right as indicated by his velocity, so his velocity is +5m/s. He is also accelerating to the left which is the opposite direction to his velocity so his acceleration is -1.2m/s2 to the right.
Since his acceleration is negative relative to his velocity and direction of motion, his speed is decreasing and he is slowing down.
Hope this helped!
1. A boy is standing on top of a roof that is 4.5 m high. If he throws a 1.4 kg water balloon down with a velocity of 2m/s,
what velocity will the water balloon strike the ground with? (ignore air resistance)
Answers
Answer:
The magnitude of the final velocity of the water balloon is 84.3 m/s.
Explanation:
To calculate the velocity of the water balloon when it strikes the ground we need to use the next equation:
[tex] v_{f}^{2} = v_{0}^{2} - 2gh [/tex]
Where:
[tex]v_{f}[/tex]: is the final velocity =?
[tex]v_{0}[/tex]: is the initial velocity = 2 m/s
g: is the gravity = 9.81 m/s²
h: is the height = 4.5 m
By entering the above values into equation (1) we have:
[tex] v_{f}^{2} = v_{0}^{2} - 2gh = (2 m/s)^{2} - 2*9.81 m/s^{2}*4.5 m = -84.3 m/s [/tex]
The minus sign is because the direction of the velocity vector is in the negative vertical axis.
Therefore, the magnitude of the final velocity of the water balloon is 84.3 m/s.
I hope it helps you!
g volume of 0.025 m3. If the temperature of the gas is 290 K, what is the rms speed of the gas atoms
Answers
This question is incomplete, the complete question is;
Argon gas (a monatomic gas) is sometimes used to insulate a double-pane window for purposes of insulation. In a particular window, the space in between two glass sheets has a volume of 0.025 m³.
If the temperature of the gas is 290 K . what is the rms speed of the gas atoms ?
The atomic mass of Argon is 39.9 u.
(1 u = 1.66 x 10⁻²⁷ kg) Enter your answer in m/s.
Enter your Answer in m/s
Answer: the rms speed of the gas atoms is 425.754 m/s
Explanation:
Given that;
mass of Argon = 39.9 u
and 1 u = 1.66 x 10⁻²⁷ kg
so 39.9 × 1.66 x 10⁻²⁷ kg = 6.6234 x 10⁻²⁶
Temperature T = 290 K
Now
V_rms = √( 3KT / M)
where Boltzmann's constant K = 1.38 × 10⁻²³ m²kg s⁻² K⁻¹
so we substitute
V_rms = √( 3 × 1.38 × 10⁻²³ × 290 / 6.6234 x 10⁻²⁶)
V_rms = √( 181266.419)
V_rms = 425.754 m/s
Therefore the rms speed of the gas atoms is 425.754 m/s
Two train whistles have identical frequencies of 220 Hz. When one train is at rest in the station sounding its whistle, a beat frequency of 10.0 Hz is heard from the other train that is approaching the station. What is the speed of the approaching train? Assume that the speed of sound is 340 m/s.
Answers
Answer:
Speed of the approaching train = 15.45 m/s
Explanation:
Given:
Frequency F0 = 220 Hz
Beat frequency F1 = 10.0 Hz
Find:
Speed of the approaching train
Computation:
Approaching frequency F2 = 220 + 10.0 Hz
Approaching frequency F2 = 230 Hz
Doppler shift;
F = [(v+v0)/(v-vS)]F0
230 = [(340+v0)/(340-0)]220
V0 = 15.45 m/s
Speed of the approaching train = 15.45 m/s
How does cyanoacrylate compare to the elements
that make it up?
HELPPPPP NOWWWWW
Answers
Explanation:
It exists in the tube as single molecules in liquid form. But when they come into contact with water, the molecules react with hydroxide ions to form long polymer chains that set into a hard solid. As there is a thin layer of moisture covering most surfaces, cyanoacrylate can bond them together very effectively.
Max observes a spaceship traveling toward him at 0.75c. He measures its length and finds that the spaceship is 250 m long. The ship brakes hard and skids to a stop on a nearby airstrip. Max remeasures the spaceship. What length does he find
Answers
Answer:
380m
Explanation:
We have the speed of the spaceship v = 0.75c
Max measures contracted length L of the spaceship as it travels
We have been given L = 250m
As this ship stops he is going to get exact length of the ship = Lol
We solve using this formula
L = Lo√ 1-v²/c²
From the formula above we make Lo subject of the formula
When we input values
Lo = 250/√1-(0.75c/c)²
= 250/√1-(0.75)²
= 250/√0.4375
= 250/0.6614
= 377.98
This is approximately 380
19 "Made mostly of ice", fits best under which heading in the table below?
Asteroid
Meteor
Comet
Planet
Description
A Asteroid
B Meteor
C Comet
D Planet
Answers
Comets are frozen leftovers from the formation of the solar system composed of dust, rock and ices. They range from a few miles to tens of miles wide, but as they orbit closer to the sun, they heat up and spew gases and dust into a glowing head that can be larger than a planet.
1. Final position minus the initial position is called
Answers
If the lead bar was heated to a temperature of 120 degrees Celsius, what would happen to its volume, mass and density?
Answers
On heating a lead bar, its volume increases, density decreases and its mass remains constant.
According to Ideal gas equation,
pV = nRT
ρ = m / V
V = Volume
T = Temperature
ρ = Density
m = Mass
Based on Ideal gas equation, Volume is directly proportional to Temperature. As temperature increases, volume also increases. Based on density formula, Volume is indirectly proportional to Density. As Volume increases density decreases.
In any reaction, the mass is always conserved. Because, mass is the amount of matter present in a substance. During a reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed, just rearranged. So the mass always remains constant.
Therefore, if a lead bar was heated to 120°C, its volume increases, density decreases and its mass remains constant.
To know more about Ideal gas equation
https://brainly.com/question/15379358
#SPJ1
Help Me Please
8th grade science, one question